This article is for HR leaders in need of a clutter-buster of their organisation skills and competencies framework.
Who needs a superpower to bring context, order, and clarity to jobs and talent and transform chaos into structure?
Just as organising your email brings peace and productivity by categorising messages into urgent, deferable, leisure, and spam, a similar principle can drastically improve workplace efficiency and decision-making.
The Essence of Organising
Organising simplifies our work lives by reducing decision fatigue, applying a simple yet effective system to manage daily choices. This quest for simplicity isn’t just a human desire; it extends into the digital realm, shaping the way Artificial Intelligence (AI) functions and enhances our lives.
AI and Decision Fatigue
Though AI does not experience decision fatigue in the traditional sense, it thrives on structured guidance. A well-organised framework allows AI to process data, predict outcomes, and interact more efficiently, generating higher-quality responses. The concept of decluttering, thus, becomes a cornerstone for enhancing AI’s decision-making capabilities.
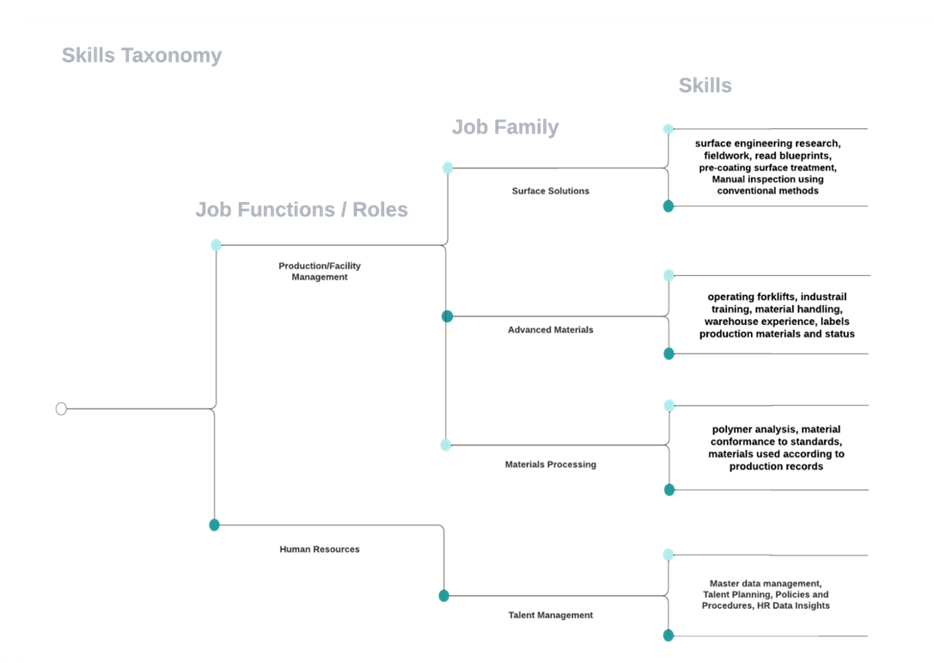
The Role of Skill Taxonomies
How can we map the extensive skills landscape in a way that promotes understanding, growth, and innovation?
The challenge is usually outright chaotic, it is a true maze to organise job, talent, skills, competencies and learning paths. Because skills are every organisation’s database, it is saved someplace whether in a well-structured format or not.
Solution: Introducing EVA.ai Skill Taxonomy Feature
The Skill Taxonomy is a framework that is not merely a list but a strategic structure that facilitates the navigation of hierarchies and the interdependencies of skills.
Skill taxonomy gives structured clarity and a universal language for categorising skills by domains and proficiency levels, offering clear pathways from foundational to advanced competencies. If you have been citing MS Office Tools as a “skill” or have a catch-all term for “Leadership”, it is time to rehash and detail the range of expertise.
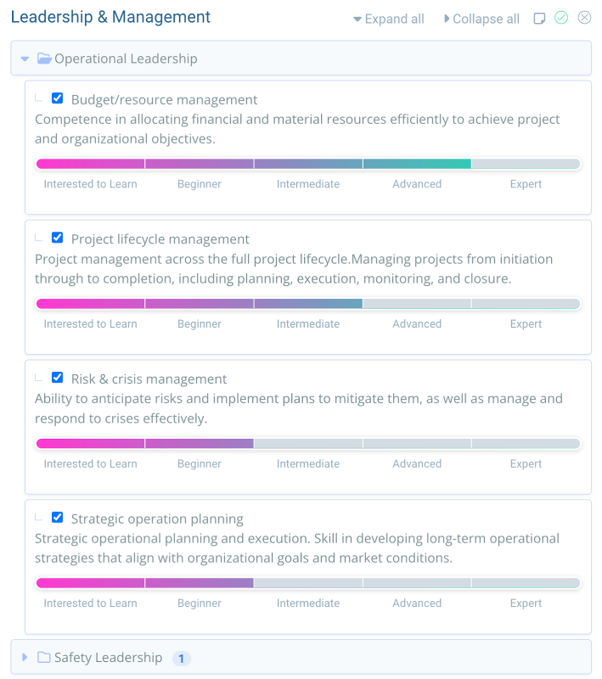
Often, expertise can be vaguely defined, missing out on the richness of your experience. There might even be unique terms or job titles specific to your organisation (like Chief Listening Officer or Storyteller) that aren’t immediately recognisable to outsiders. It’s crucial to unpack these terms, offering a clear view of their skills and responsibilities, to ensure your full spectrum of abilities is accurately and compellingly presented.
Individuals, HRs, and Organisations can leverage taxonomies to identify, develop, and leverage skills with precision and foresight.
How does AI benefit from this structure?
Structured skill data is invaluable for training AI algorithms, and enhancing their efficacy. Consider the difference between generic prompts and those meticulously crafted to embody inclusivity, diversity, and specificity. Human input and AI results work in synergy, enrich AI’s understanding and application and grant it greater autonomy.
The Impact on HR and AI-augmented Jobs
Skill taxonomies influence several areas:
- Enhanced Job Profiling and Talent matching accuracy
- Improved Natural Language Processing (NLP) capabilities for deeper context and intent comprehension
- Automate analysis of skill gaps/underperforming areas
- Insight into the skills that are difficult to hire because of niche/poor branding
- Future-proof talent decisions. For example, prepare for a hiring spike demand, build talent pools of a particular skill category
- Tailored content for personalised career pathways and learning programs
Developing a Skill Taxonomy: Strategies for Success
We’ll share with you the best strategies that have allowed organisations working with us at EVA.ai to develop their skill taxonomy and plug in AI for impact and automation.
- Establishing Skill Groups
Grouping by Nature and Team: Begin by classifying skills according to their type (e.g., technical, communication) and the teams that benefit most from them (e.g., sales, engineering). This initial organisation aids in understanding the diverse skill sets within your organisation and their contributions to different functions.
It highlights skills distribution so you can instantly pick the areas that need reorganisation, cross-training, or opportunities for automation like augmenting the job tasks with a co-pilot or ChatGPT.
Additionally, it assists in recognising mismatches in current roles, guiding internal reassignments, and enhancing external recruitment strategies by developing skill-specific assessments and interview questions.
Hierarchical Classification: Develop a skill hierarchy that spans from beginner to advanced levels. This structure not only helps identify skill gaps but also supports targeted training and development efforts.
Contribution to Growth and Demand: Evaluate how each skill or skill group contributes to organizational growth and market demand. This assessment assists in prioritizing the skills that are most valuable and impactful.
Must-Have vs. Good-to-Have: As McKinsey suggests, in the realm of skills-based hiring, focus is placed on the most critical or scarce skill for a specific role rather than seeking a candidate with all possible skills. Distinguishing skills as must-have, good-to-have, and nice-to-have offers a strategic approach to talent acquisition and development.
- Utilizing Data and Defining Skill Families
Data Curation: Utilize existing data from Human Resources Information Systems (HRIS), job descriptions, talent profiles, and resumes to inform your skill taxonomy. This curation process sparks ideas for organising and broadening your taxonomy framework.
Skill Families and Tags: Establish intuitive, high-level groups or ‘families’ of skills. Attach tags to these families easily understood and referenced by your team. This ensures the taxonomy is practical for both human use and AI applications, making it both user-friendly and accessible.
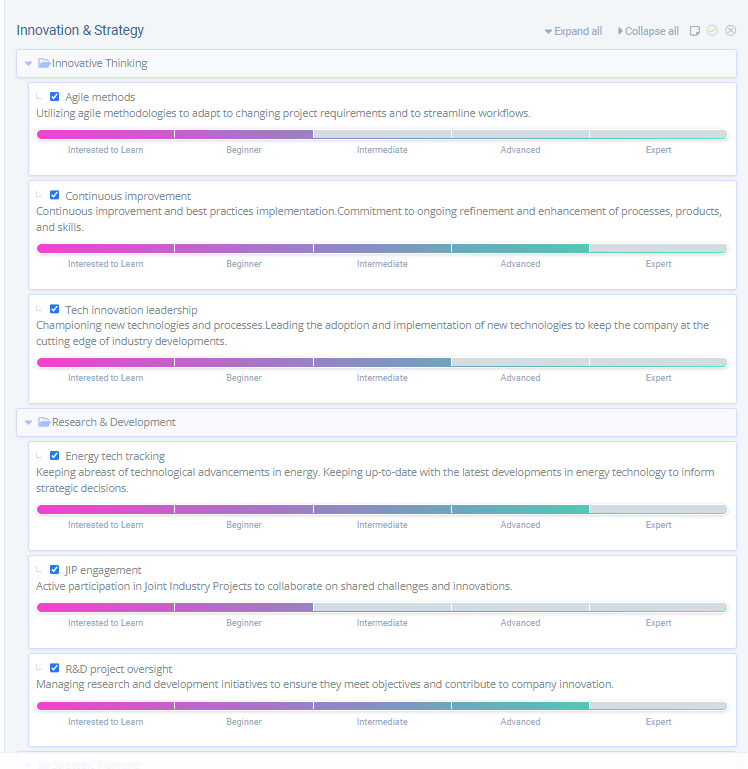
The EVA.ai interface provides a visual representation of Digital Skill Taxonomies. These are intricately linked to talent profiles and job descriptions, enabling highly accurate AI-driven matching.
3. Planning for Future Competency Levels
Introducing Competency Levels: Prepare for the inclusion of future competency levels and more complex skill types. Hierarchically organising skill categories facilitates a deeper understanding of potential career progression and skill development opportunities.
Core and Futurist Skills: Identify skill groups that are central to your organisation’s domain, as well as stand-alone and forward-looking skills where your organisation intends to be a market leader.
This ensures preparedness for emerging trends and hiring needs. Consider whether you plan to acquire these skills externally, develop them within your organisation, find adjacent skills or utilise internal rotation strategies to meet these needs.
4. Improving Job Profiles and Descriptions
Incorporating skill taxonomies into your job descriptions sets clear expectations upfront. Furthermore, it enables candidates to self-assess their skills and proficiency levels during the application process. By inviting applicants to actively evaluate and rate their expertise in both depth and breadth as they review the job profile, recruiters gain a head start in screening and shortlisting candidates. This approach not only clarifies the role’s requirements but also streamlines the recruitment process by quickly identifying those who best match the job’s skill needs.
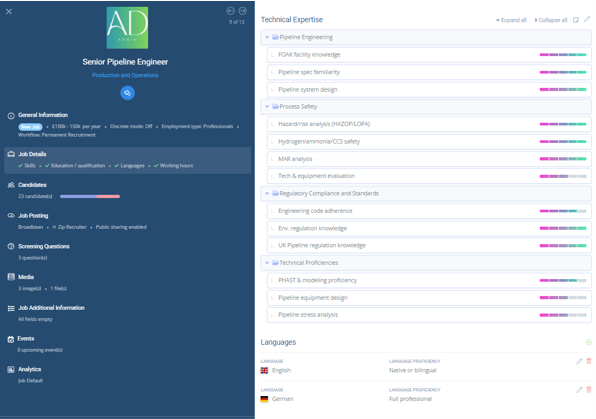
Illustration of EVA.ai’s interface reflecting the skill taxonomies on a specific job for candidates/applicants to self-evaluate.
5. Precision in AI matching and recommendations
Talent Matching on Point: AI algorithms can be calibrated to align with your skill taxonomy, enhancing their ability to accurately comprehend and interpret job requirements accurately. Skill taxonomies serve as a crucial criterion for matching, enabling the precise fit-check of talent for specific skill sets, nuanced evaluation of related skills, and identification of complementary competency levels. This results in a more efficient and effective talent-matching process.
Advantages: Precise job-talent matching through AI yields highly relevant, personalized job recommendations and learning opportunities.
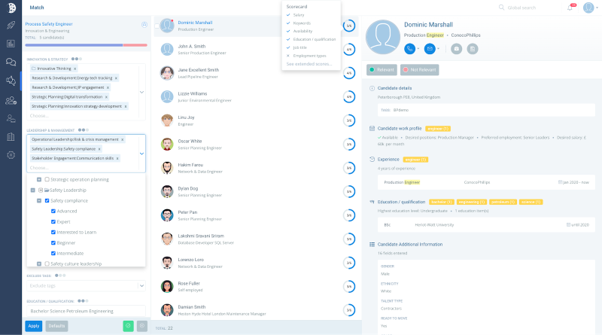
Illustration: On EVA.ai, AI-driven talent matching automatically populates skills for selection based on the skill taxonomy, streamlining the process.
Tailored Learning Paths: Leverage the skill taxonomy framework to prompt EVA to suggest learning and development strategies. By focusing on the discrepancies between an employee’s current skills and their job aspirations, EVA can automate the creation and distribution of customized career development paths for employees, aligning with their professional goals.
Observation and Prediction: The organised structure of skills aids in monitoring trends, including in-demand skills, roles that are difficult to fill, and timeless skill sets. This strategic analysis is instrumental in anticipating industry demands and making proactive preparations.
Governance of Sustainable Skill Taxonomies
The development of the skills engine feature within the EVA.ai platform highlights the importance of dynamic skill structure governance and maintenance. This feature grants admin privileges to your A-team to create, deliberate, and approve skill structures, ensuring the framework remains agile and reflective of your organisation capacity.
Acknowledging the necessity of regularly updating your skill taxonomy to reflect current realities, if there are suspected gaps in your data due to recent changes or overlooked employee updates, leverage EVA Engagement strategies powered by Conversational AI to initiate talent campaigns and collect new skills information, ensuring your taxonomy and skill database remains relevant and comprehensive.
With EVA.ai, updating your skill taxonomy doesn’t mean starting on a blank canvas. You can achieve a refined and relevant skills taxonomy in less than three weeks by harnessing the most recent skill data from within your organisation.
What is the IMPACT? RISK? COMPLEXITY? in implementing this use case? Let’s evaluate based on what you need.




